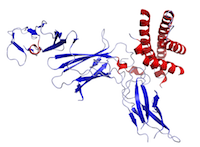
Interleukin 6
 The history of interleukin-6 (IL-6) dates back to the late 1960s when it was hypothesized that a T cell-derived soluble factor would be involved in B cell activation, which was initially named B cell stimulatory factor-2 (BSF-2). In 1986 the complementary DNA encoding this factor was cloned and the name IL-6 was introduced.
The history of interleukin-6 (IL-6) dates back to the late 1960s when it was hypothesized that a T cell-derived soluble factor would be involved in B cell activation, which was initially named B cell stimulatory factor-2 (BSF-2). In 1986 the complementary DNA encoding this factor was cloned and the name IL-6 was introduced.
Figure This is a crystal structure of human IL-6 created using the data from Protein Data Bank (PDB: 1ALU) and rendered using PyMOL.
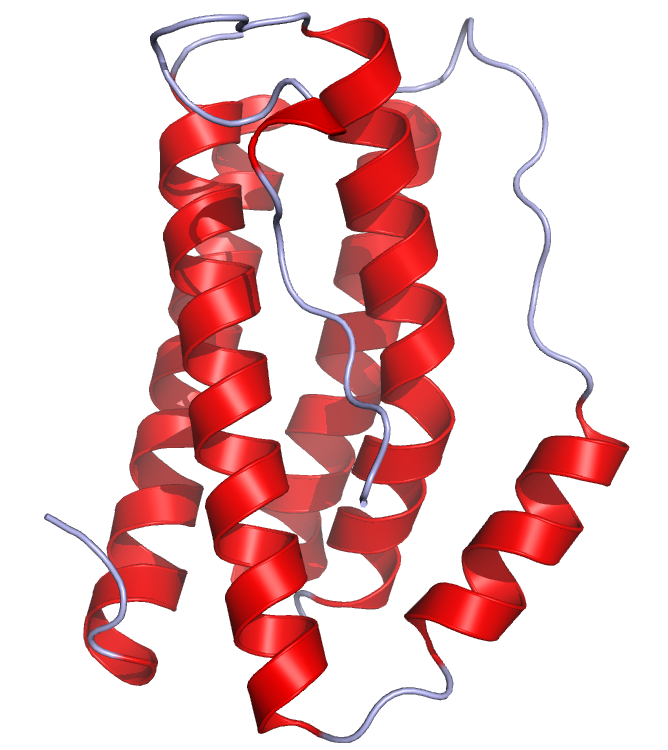
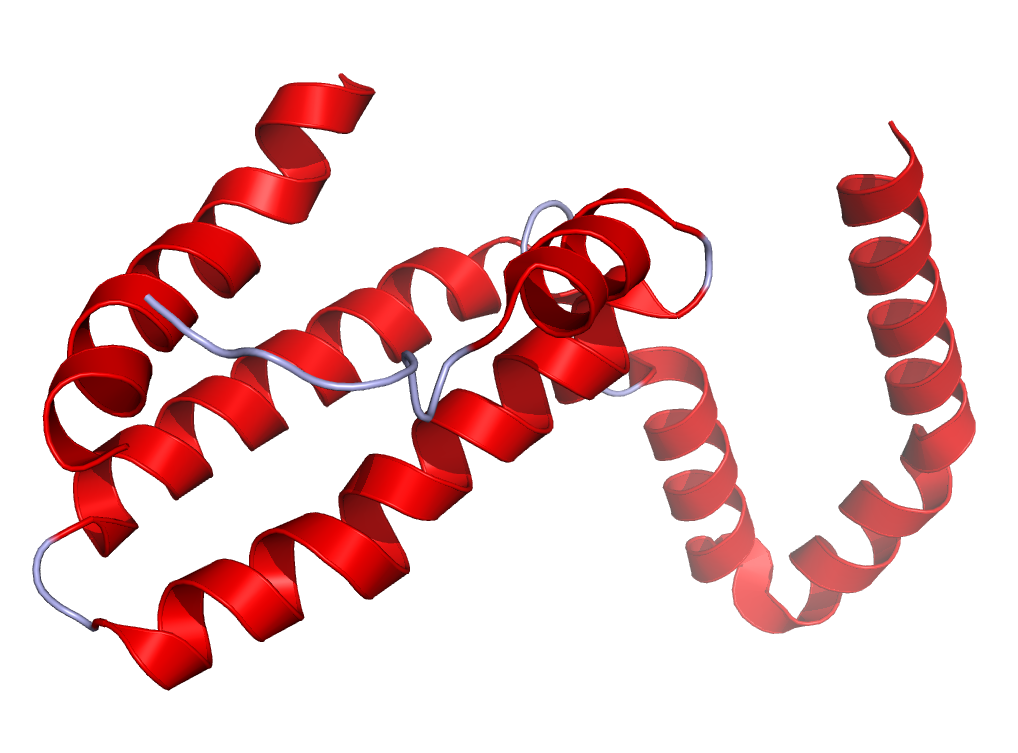 Interleukin-10 (IL-10), also known as human cytokine synthesis inhibitory factor (CSIF), is a cytokine encoded by the IL-10 gene in humans, located on chromosome 1. The protein has a length of 178 amino acids and functions as a homodimer.
Interleukin-10 (IL-10), also known as human cytokine synthesis inhibitory factor (CSIF), is a cytokine encoded by the IL-10 gene in humans, located on chromosome 1. The protein has a length of 178 amino acids and functions as a homodimer.